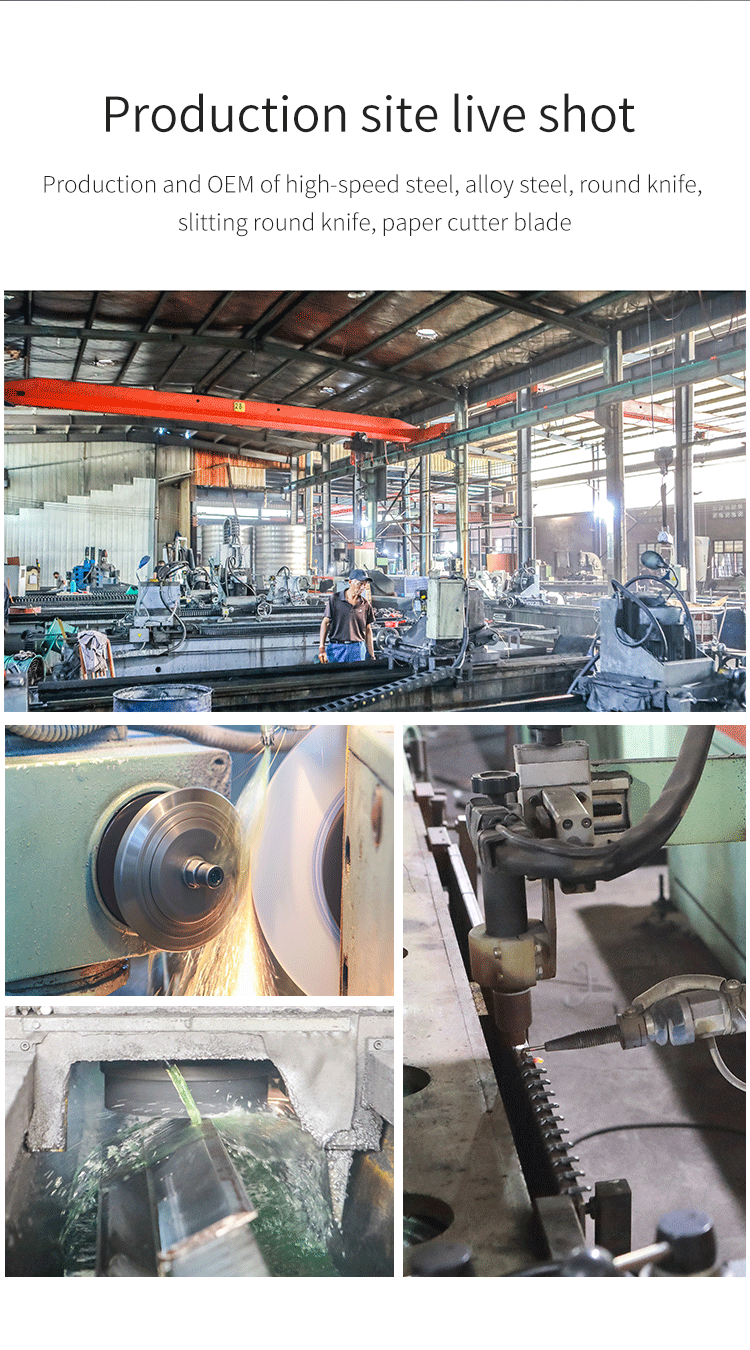
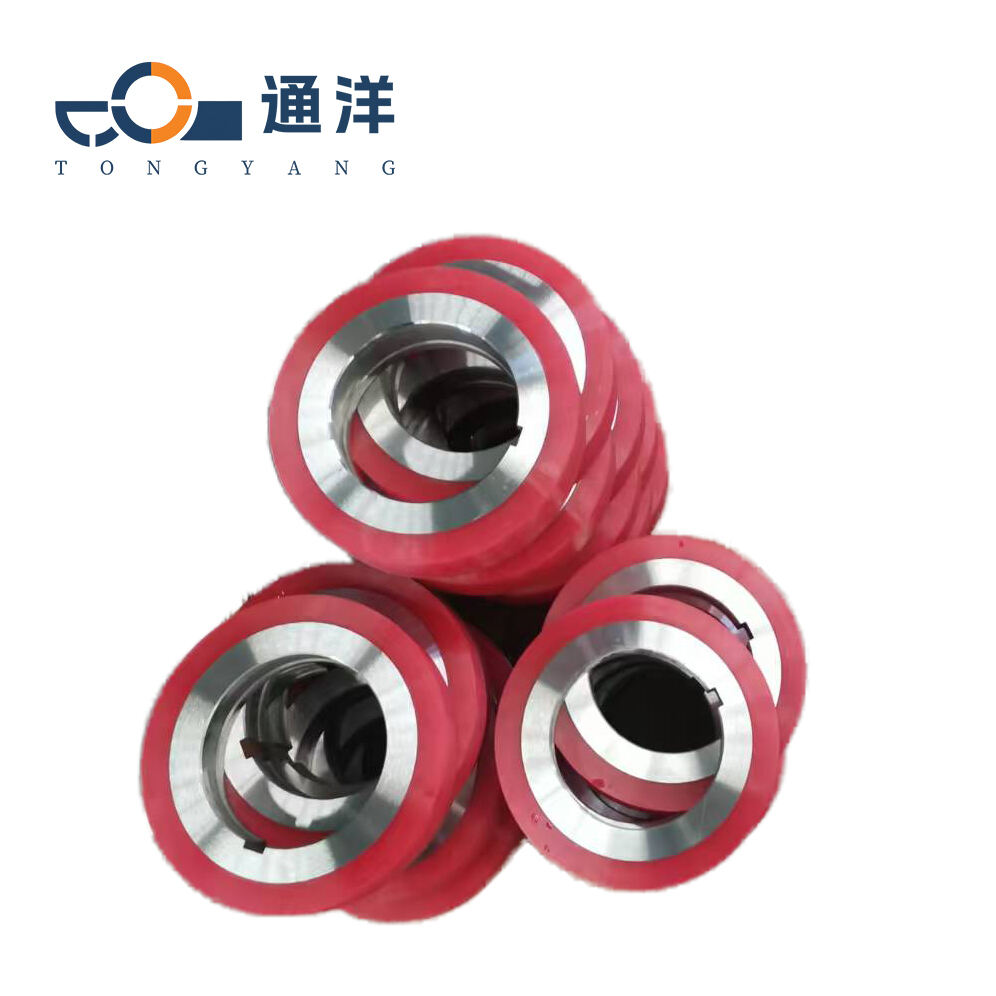
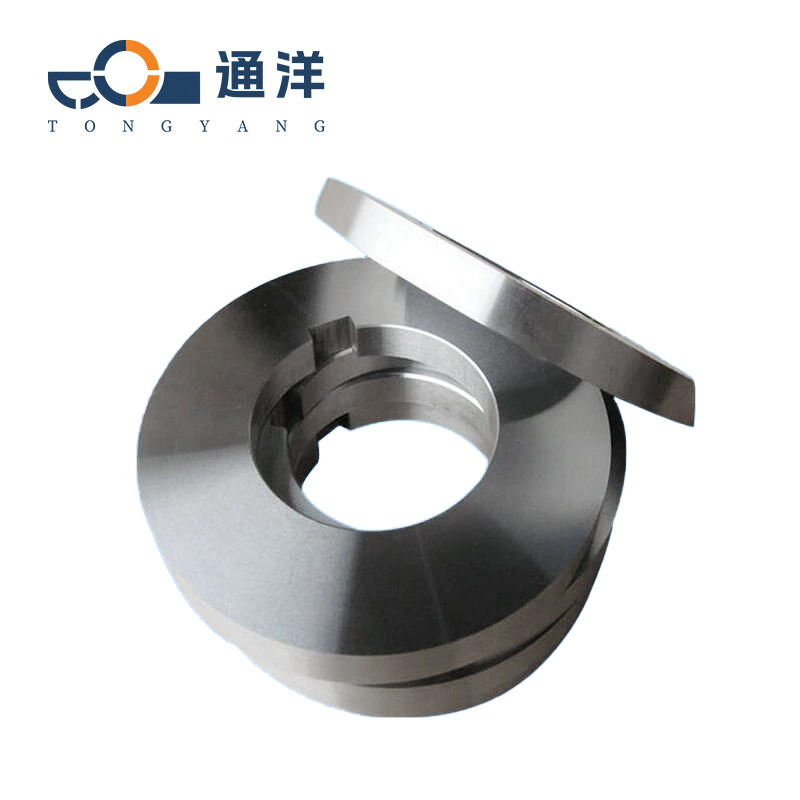
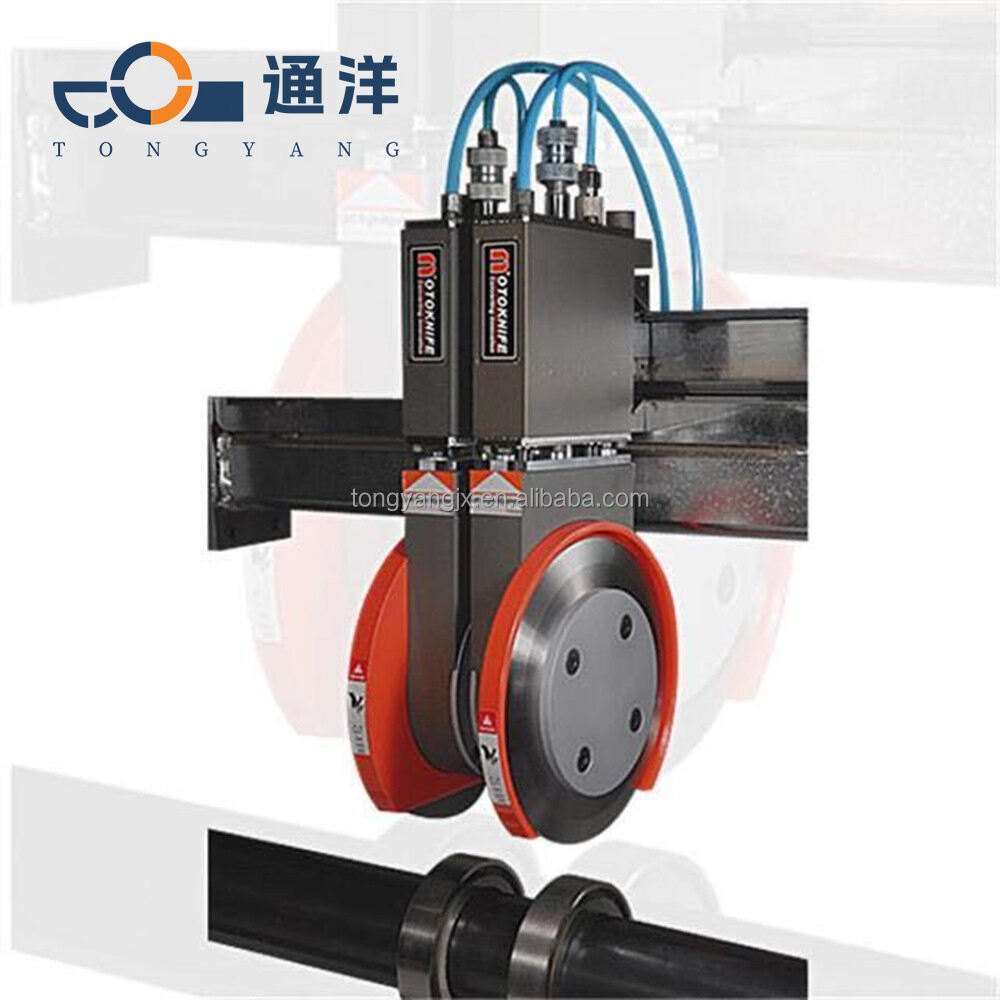
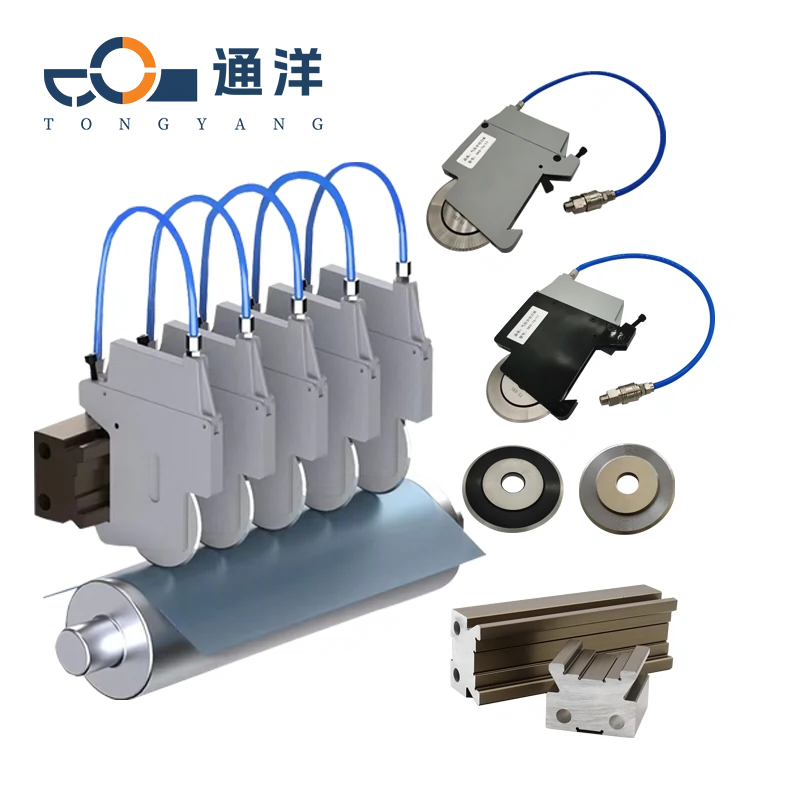
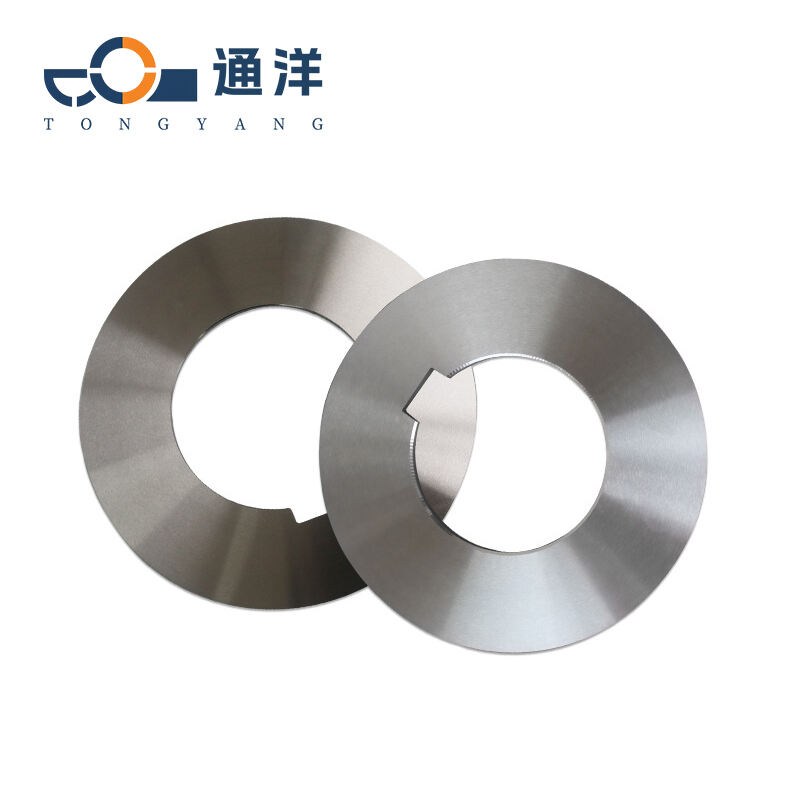
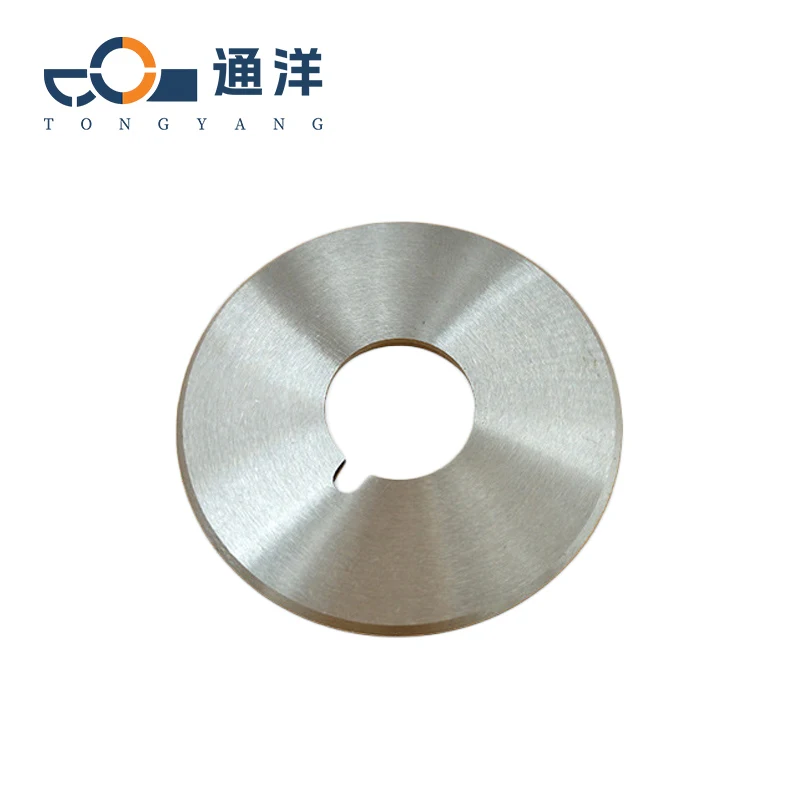
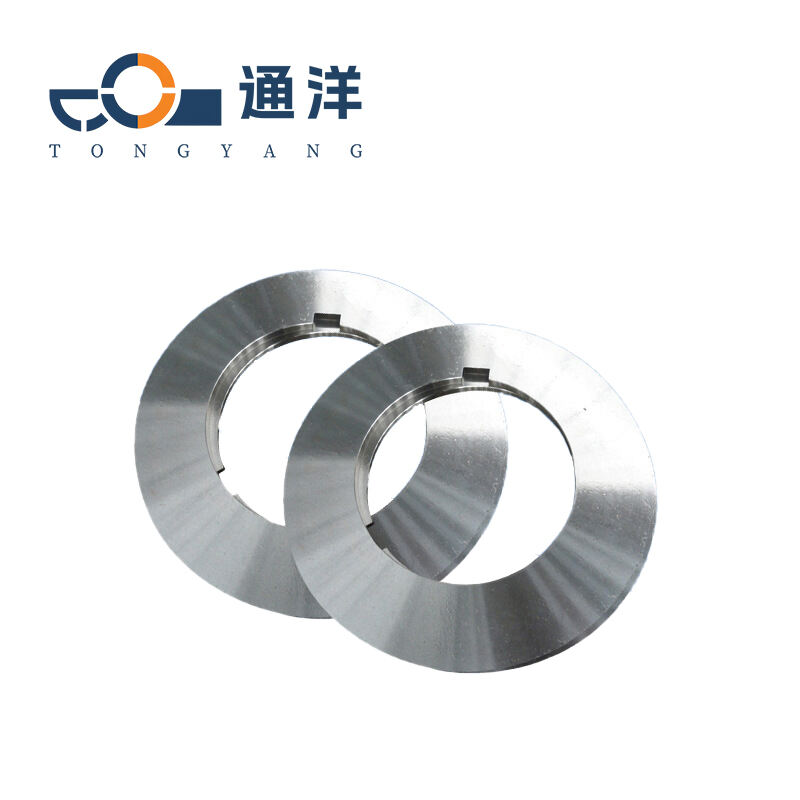
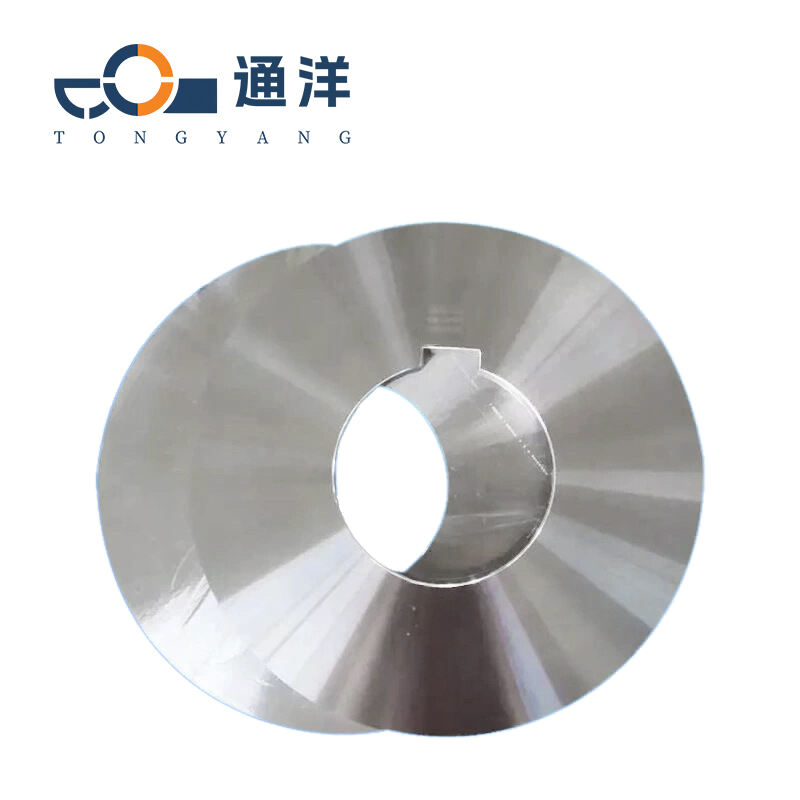
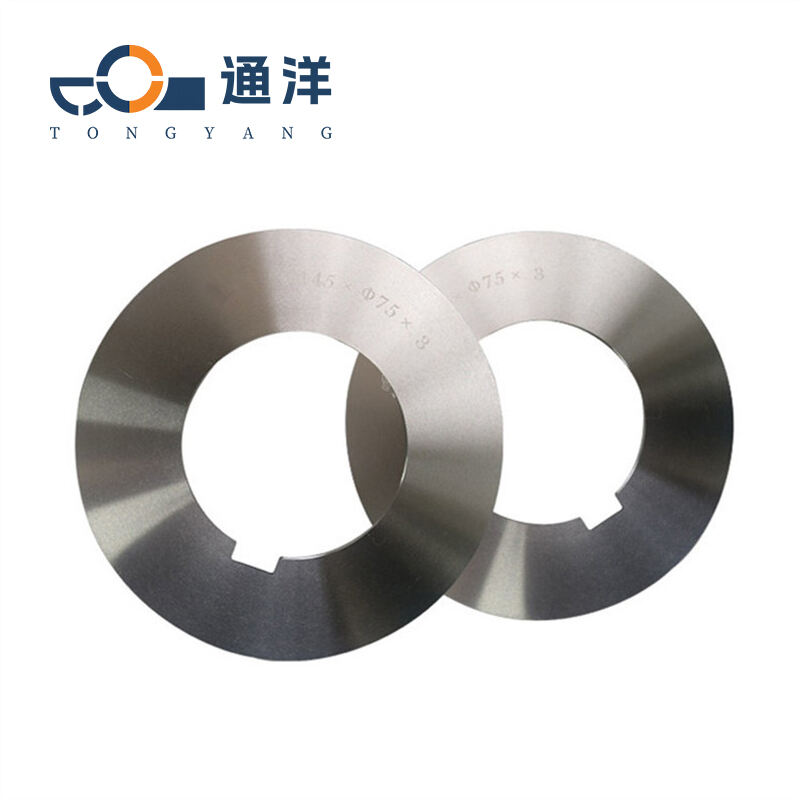
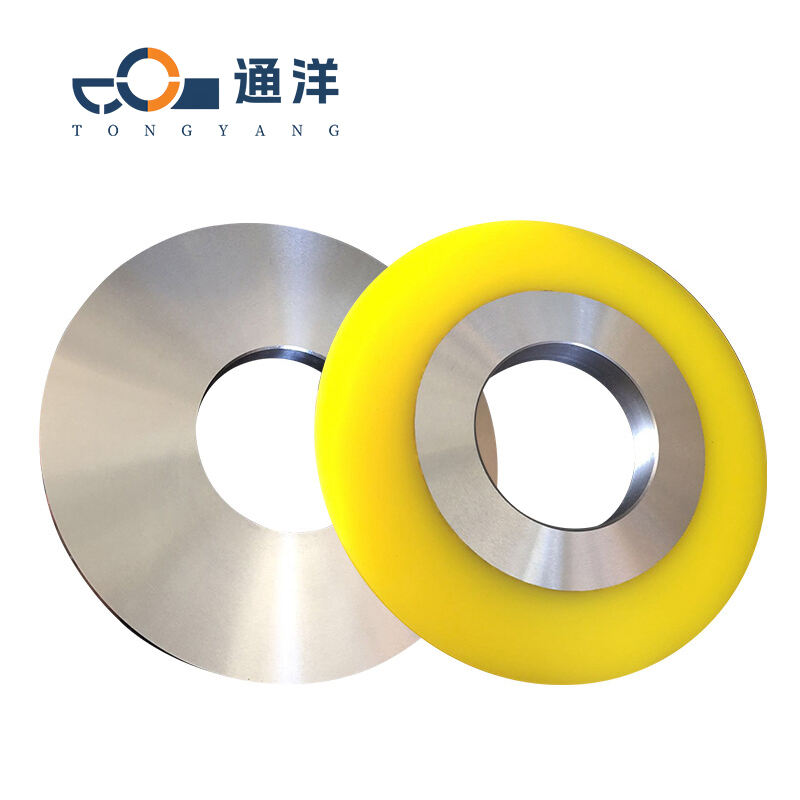
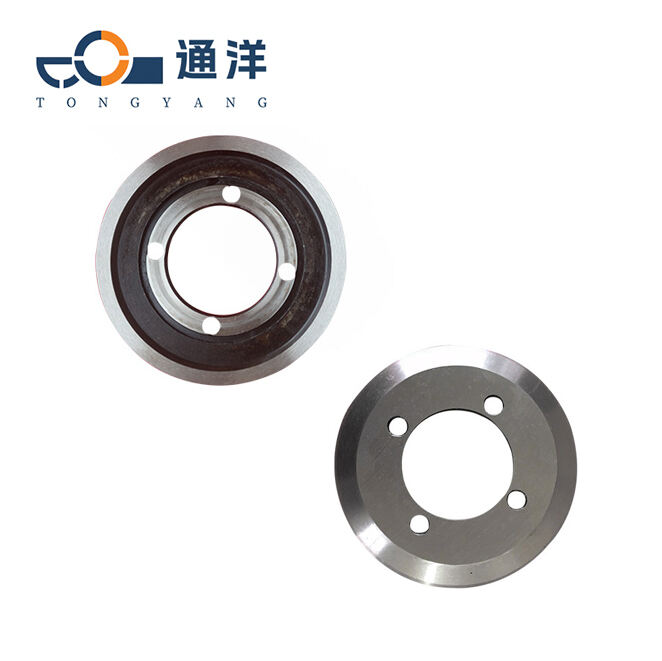
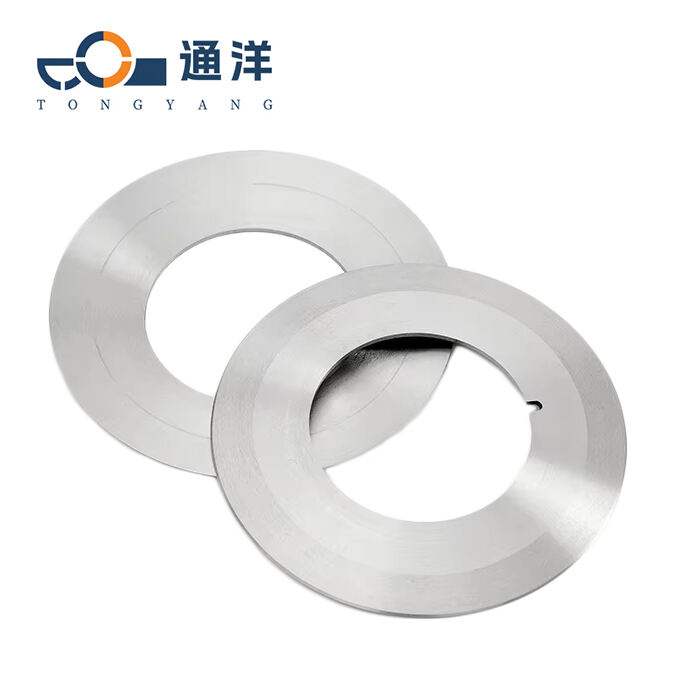
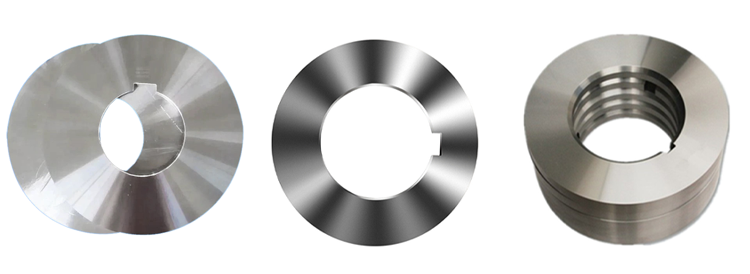
Circular metal slitting knife
This circular metal slitting blade is made of carefully selected high-quality steel. Through precise forging and advanced heat treatment processes, it features high hardness and strong wear resistance. The cutting edge is sharp and precise, enabling efficient slitting of metal coils, and it is widely used in industries such as metal processing.
- Overview
- Recommended Products
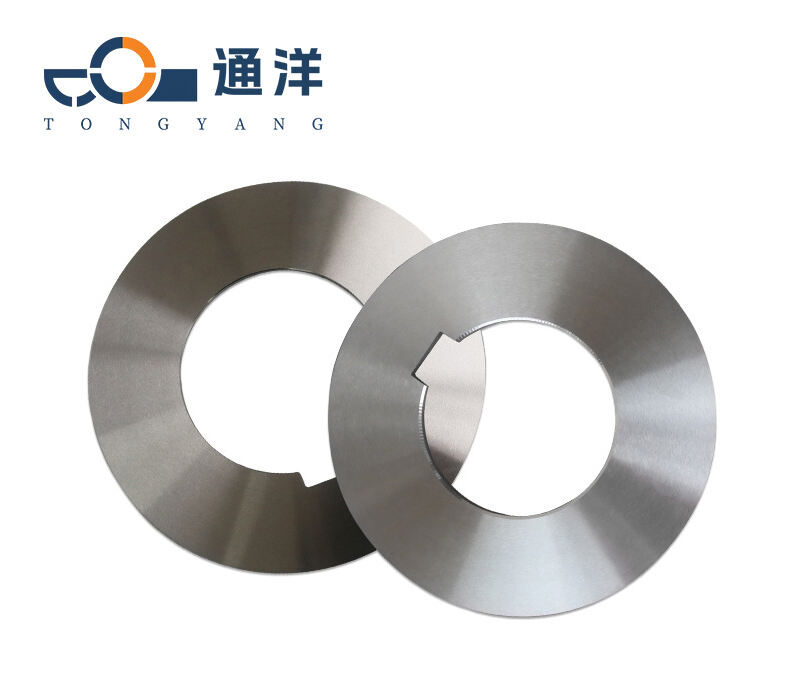
Common material types
| Material | Classic brand | Hardness | Features and applicable scenarios |
| Tool steel | SK5、SK7 | 55-60 | It has a low cost and a sharp cutting edge. It is suitable for low-speed cutting (< 50m/min) of soft metals (low-carbon steel, copper). |
| High-speed steel(HSS) | M2、M42 | 62-68 | It can withstand high temperatures (600°C) and is wear-resistant. It is suitable for medium-speed cutting (50-150m/min) of structural steel, thin stainless steel plates, etc. |
| Cemented carbide | YG8 (WC-Co)、YT15 | 89-93HRA (≈HRC70-75) | It has extremely high hardness and wear resistance. It is suitable for high-speed cutting (150-300m/min), such as quenched steel, cast iron, and thick stainless steel plates. |
Common dimensions, models and specifications
General specifications
| Norms | Range (Common Values) | Applicable materials |
| Diameter(Φ) | 50-600mm(The commonly used value is 100-400mm. ) | For thin plate cutting: Φ100-200mm; For thick plates/high-speed equipment: Φ200-400mm |
| Thickness(mm) | 1-10mm(Choose according to the thickness of the metal. ) | For thin plates (< 3mm): 1-3mm; for medium-thickness plates (3-10mm): 3-6mm; for thick plates (> 10mm): 6-10mm. |
| Hole diameter(D) | 15-100mm (Match the diameter of the shaft of the equipment. ) | The commonly used values are: 20mm, 25mm, 32mm, 50mm (suitable for large-scale equipment). |
| The angle of the cutting edge | Rake angle: -5° to +15°; Clearance angle: 5° - 15° | For hard metals (such as quenched steel): negative rake angle (-5° to 0°); for soft metals: positive rake angle (+5° to +15°) |
Cutting edge design
Flat edge: A general-purpose type, suitable for smooth metal surfaces (such as aluminum plates and thin sheets,stainless steel plates).
Saw-toothed edge: Increases the cutting force and prevents slipping. It is suitable for thick plates (5mm) or metals with high hardness (such as cast iron).
Coated edge: TiN (general-purpose), TiAlN (resistant to high temperatures), CrN (corrosion-resistant), which can reduce friction and tool adhesion (for example, when cutting stainless steel).
Wave-shaped edge: Reduces the cutting resistance and is suitable for cutting multi-layer stacked metals (such as automotive sheet metal).
Special specifications
Combination cutter: Multiple pieces are stacked (such as 2-5 pieces), which are used for synchronous cutting of multi-layer metals (such as the sheet metal of power distribution cabinets).
Stepped cutter: The cutting edge is in a stepped shape, which is suitable for processing metals of different thicknesses (such as the grooves of the contours).
Ultra-thin cutter: With a thickness of less than 1mm, it is used for cutting precision electronic components (such as copper foils and aluminum strips).
Selection suggestions (according to the type of the metal being cut)
| material | Recommended Materials: | Typical Model (Φ×T×D) | Cutting speed (m/min) |
| mild steel | High Speed Steel (M2) / Tungsten Carbide (YG8) | Φ150×3 mm×25 mm | 80-200 |
| stainless steel | Tungsten carbide (YT15) + TiAlN coating | Φ200×5 mm×32 mm | 50-150 |
| cast iron | Tungsten carbide (YG6X) / CBN | Φ250×6 mm×50 mm | 30-100 |
| Aluminum alloy | Diamond (PCD) / High Speed Steel (TiN Coating) | Φ300×4mm×50mm (High Speed) | 200-500 |
Maintenance and precautions
The most important thing in the metal cutting process is to cool down (using water or oil cooling) to Prevents the cutting edge from overheating, which can affect cutting performance and service life Cutting blades. During normal use, dynamic balancing should be performed for cutting blades with a diameter greater than 200mm Outside. For cutting tasks that require high precision, balancing should be performed at least once a time weeks, and measurements should be taken once a day.
Lifetime reference
High speed steel: 50-200 hours (depending on the hardness of the metal)
Carbide: 200-500 hours (30% longer service life of coated tools)
CBN / Ceramic: 500-1000 hours (in precision cutting scenario)
Customized processes